Simulating the Hosted Application
A guide to understanding and using the Hosted Application Simulation API.
A guide to understanding and using the Hosted Application Simulation API.
The Hosted Application Simulation allows you to mimic the behavior of a Hosted Application without interacting with the production APIs. All initial steps for starting a Hosted Application are identical to production, but the simulation environment provides placeholder URLs and endpoints to control state transitions.
Once the call to start the Hosted Application has been made, you will as usual receive a next parameter in the response payload. In production, this URL directs users to the Wayflyer funding web application. In the sandbox environment, the next parameter points to a placeholder page showing relevant handoff information, providing visual confirmation of a successful handover.
Once a Hosted Application has been started, the simulation API allows you to advance the application's lifecycle:
GET /v1/company/hosted-application/simulation
{
"status": "AWAITING_UW_DECISION",
"valid_actions": ["pass-uw", "fail-uw"]
}
To perform a simulation action, send a POST request to the corresponding action endpoint:
POST /v1/company/hosted-application/simulation
{
"action": "fail-uw",
}
Some actions include additional parameters to model all potential outcomes. For more detail, see the sandbox API documentation.
The full simulation lifecycle is illustrated below:
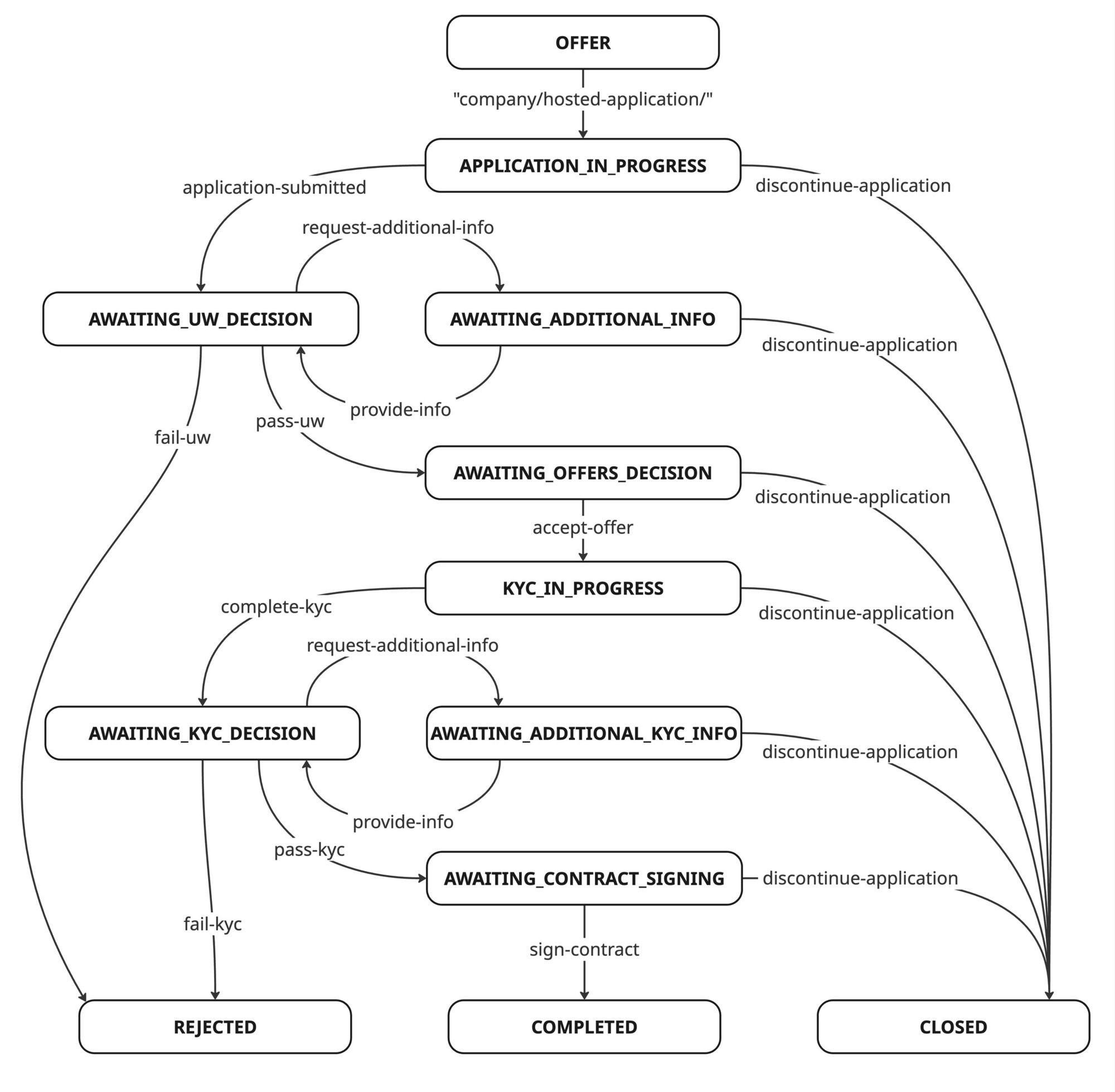
You can combine the simulation API with the CTA API to view the effect these state changes have on the behaviour of the call to action. This allows for a fully representative simulation of the entire Hosted Application lifecycle.